Night Blood Surveillance
Night blood smear collection (NBS) is essential for detecting microfilaria on a regular basis in the filariasis program due to their nocturnal periodicity in the peripheral blood circulation.
The presence of microfilaria in the peripheral blood circulation at night follows a typical nocturnal periodicity pattern. Microfilaria counts rise in the late evening, reach a peak around midnight, and gradually decline toward early morning.
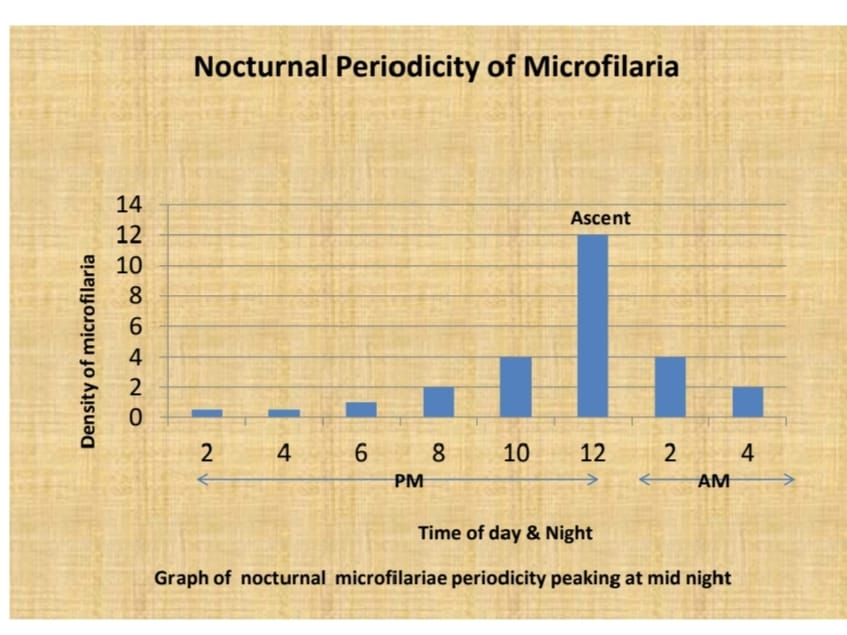
- X-axis (Time): Shows the 24-hour cycle, typically ranging from 2 PM to 4 AM
- Y-axis: Microfilaria (mf) count or mf density per unit of blood (20 μL/mf) in Peripheral Blood Smear (PBS)
Procedure of NBS Collection
Blood smears should be collected during the night, typically between 8:30 PM to 2:00 AM, when microfilariae are present in the maximum numbers in the peripheral blood circulation. The recommended time in India is often after 8:30 PM, but most international protocols suggest between 10:00 PM to 2:00 AM.
Peak Window: The highest density occurs between 10:00 PM to 2:00 AM, coinciding with the feeding times of nocturnal mosquito vectors like Culex quinquefaciatus.
This procedure is a routine activity and a part of mass screening or targeted surveillance.
- Blood is usually obtained by a finger prick.
- A thick blood smear is made using 20 microliters of blood per smear.
- The smear must be air-dried and later stained. Staining should be done within 72 hours.
- The slide should be labeled properly with the batch number and B.S. number.
After staining, the slide should be air-dried, and then it is ready for microscopic examination.
Quality of Filarial Thick Smear
Here is a detailed, step-by-step procedure for preparing thick and thin filarial blood smears based on standard guidelines:
- Place a small drop of blood (6 microliters or 12 microliters) on the center of the slide.
- Using the corner of another clean slide (spreader), spread the drop in a circular or oval shape (oval pattern) about 10 mm vertically and 20 mm horizontally in diameter.
- The filarial smear should be uniformly spread, not too thick or thin, and without cracks or holes.
- The thickness of the filarial smear should be 10–12 layers.
- Allow the smear to air dry completely at room temperature (minimum 30 minutes to several hours, depending on climatic conditions).
- Ensure proper labeling with the patient ID, date, and time of B.S. collection to maintain traceability (i.e., proper labeling with the batch number and B.S. number). After clearly labeling, all slides must be properly handled to avoid mix-up or contamination.
- Do not fix the thick smear with methanol or heat. It must remain unfixed for staining.
- Once dried, it is ready for staining.
Thin Smear: For thin films, create a feathered edge.
Staining Procedure
A) Dehemoglobinization (for Thick Smear)
- After drying, dip the slide briefly in tap water to lyse red blood cells.
- Air-dry the slide again.
Staining Options
JSB-1 Stain
- The dehemoglobinized blood smears are stained in JSB-1 for 40 to 60 seconds.
- Wash the slide gently in distilled water or tap water.
- Put it to air dry, standing upright, in the staining box or in a clean place at room temperature.
Giemsa Stain:
- Prepare a 1:10 or 1:20 dilution of Giemsa stain with buffered water (pH: 6.8 to 7.2).
- Flood the smear with stain and leave it for 30 to 40 minutes.
Wash gently with distilled water or tap water until the smear appears just pink, then air dry standing upright.
Microscopic Examination
Examine the stained B.S. under the low-power lens (10X lens) of a compound microscope for regular examination. If there is any doubt about the species or artifacts, it should be confirmed by using either the high-power lens (40X lens) or the oil-immersion lens (100X lens). The species of microfilaria (mf) is confirmed under the oil immersion lens.
The entire blood smear is to be examined systematically from one end to the other. Filarial B.S. can be examined horizontally and vertically from one end to the other, with adjacent fields closely examined.
Parasitological Indices in Filariasis
The following indices are used in filariasis surveillance:
- MF rate

- Disease Rate

- Average MF count or average MF density
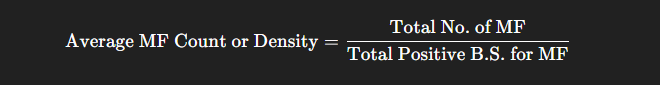
- Endemicity Rate
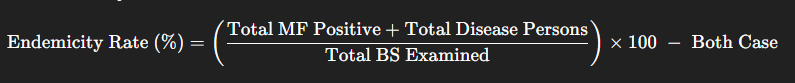
Cross-Checking of Blood Smears
- All positive slides should be sent to the office of the Regional Director of Health and Family Welfare (RDH&FW) for cross-checking.
10% of the negative slides should be sent to the state-level laboratory. The state-level laboratory will, in turn, send 2% of these slides to the office of the Regional Director of Health and Family Welfare (RDH&FW) and will examine the remaining 8%.