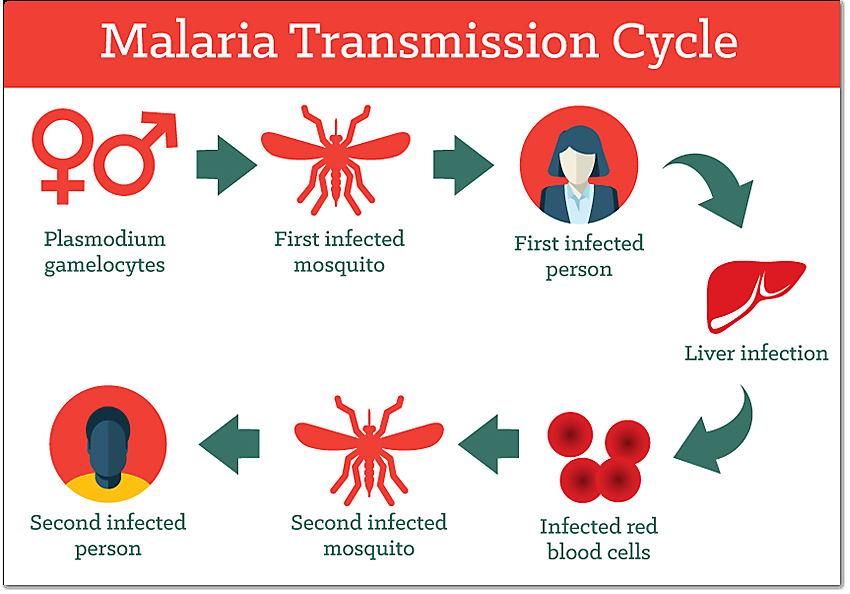
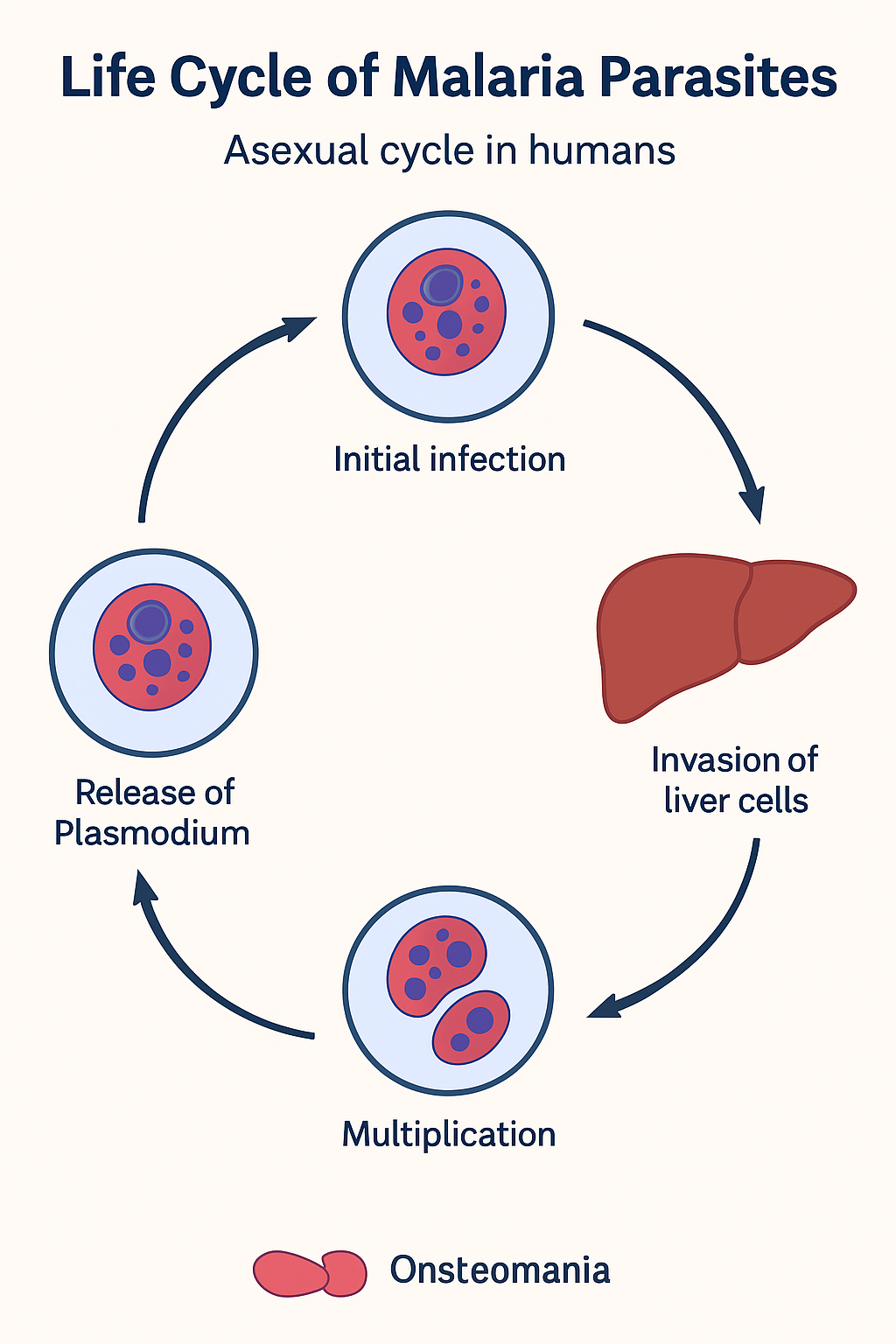
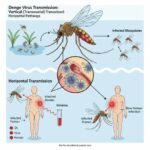
Effective prevention and control strategies used (dengue fever) in high-burden countries
High-burden countries employ a range of integrated, multi-pronged strategies for effective prevention and control vector-borne diseases like dengue fever
Integrated Vector Management (IVM )
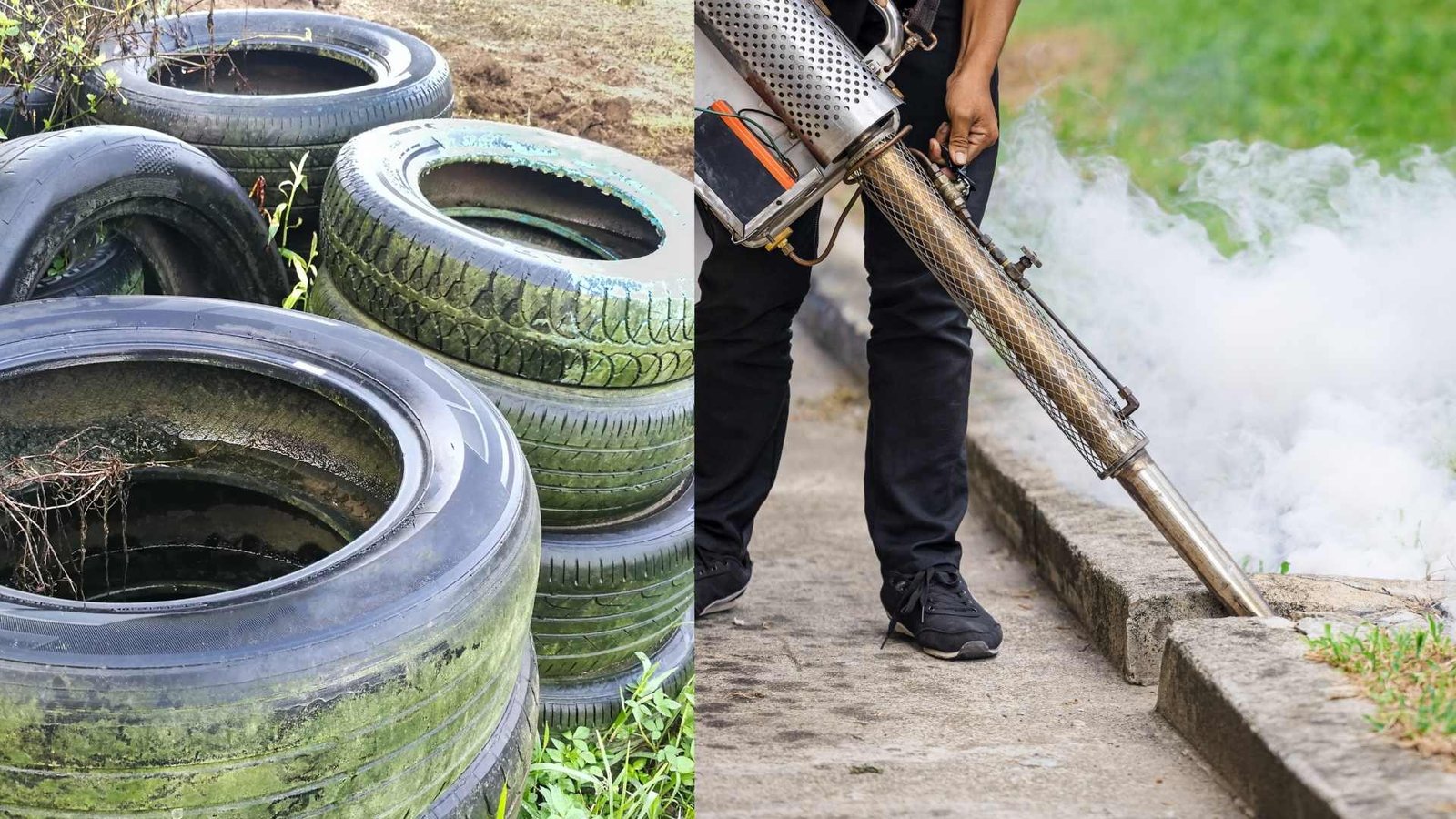
Major countries such as Brazil, Thailand, and India use IVM approaches combining targeted insecticide use, source reduction, biological control, and community participation in environmental management
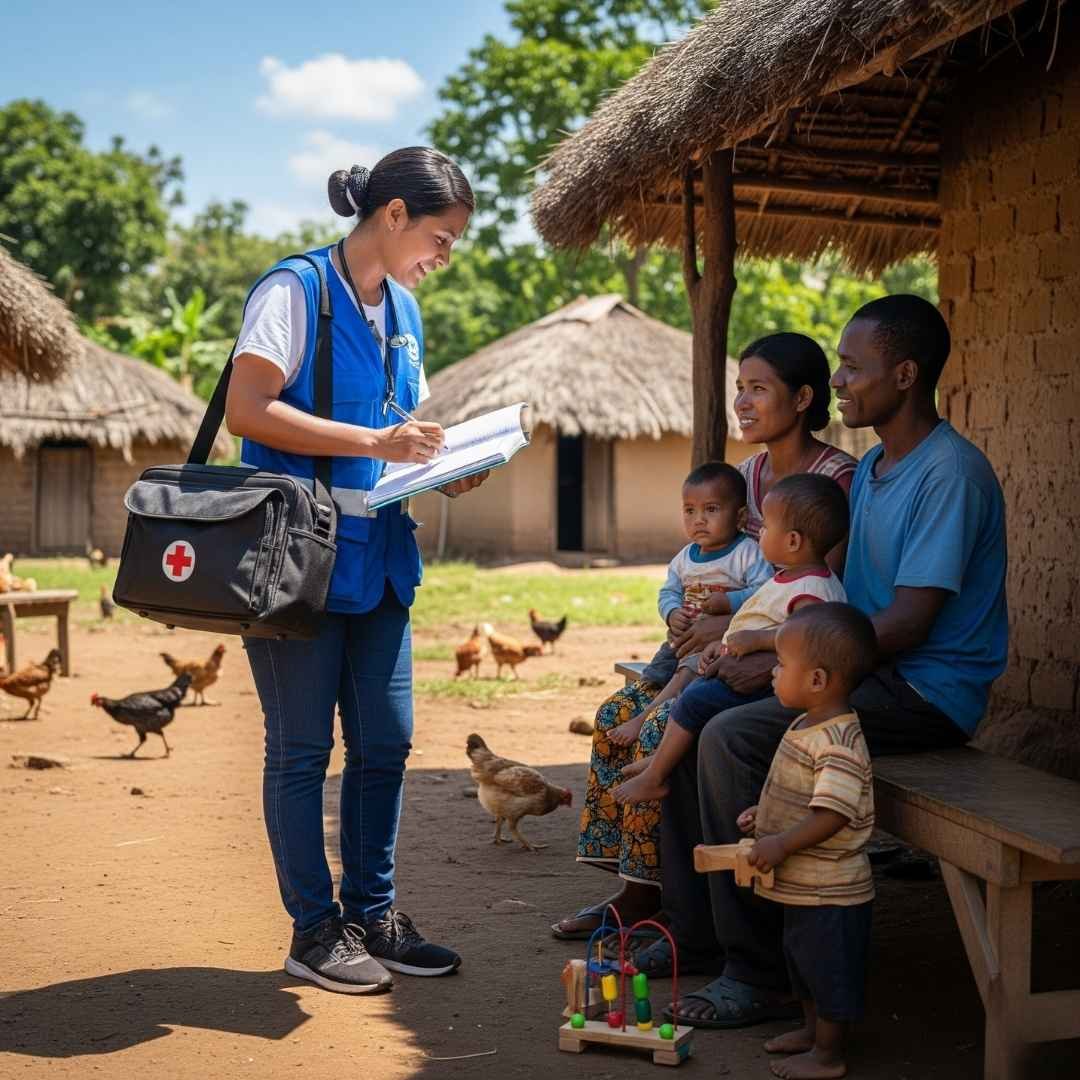
Community Mobilization and Health Education
Regular Community awareness drives, school-based education, and engagement of local leaders promote behavioral change for eliminating breeding sites, enhancing personal protection, and early care seeking for dengue symptoms
Surveillance and early Warning systems
Enhanced case and vector surveillance systems trigger rapid response to outbreaks by mapping hotspots, deploying resources, and organizing timely public alerts in high-risk zones.
Epidemic Preparedness and Rapid Response
National and regional task forces conduct seasonal risk mapping, stockpiling of diagnostic kits and supportive treatments, and training of healthcare staff in case management during the peak transmission periods.
Biological and Novel Approaches
Some high-burden regions have piloted or scaled up Wolbachia-infected Aedes mosquito releases, sterile insect technique trials, and targeted larvicidal applications for sustainable vector reduction
Vaccination
A few countries have introduced dengue vaccines for high-risk populations, though coverage and effectiveness are still evolving and require ongoing monitoring.
India’s National Control Strategy
The National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme in India deploys a package of interventions: fogging during outbreaks, intensified larval source reduction, strengthening of primary health centers or community health centers for prompt diagnosis, community-based vector surveillance, and use of guppy fish as well as use of BTI powder for larval control.
Thus, effective dengue prevention and control in high-burden settings requires a blend of vector control, public education, robust surveillance, quick clinical response, and innovative biological interventions, all anchored in strong community participation and adaptive policy frameworks.