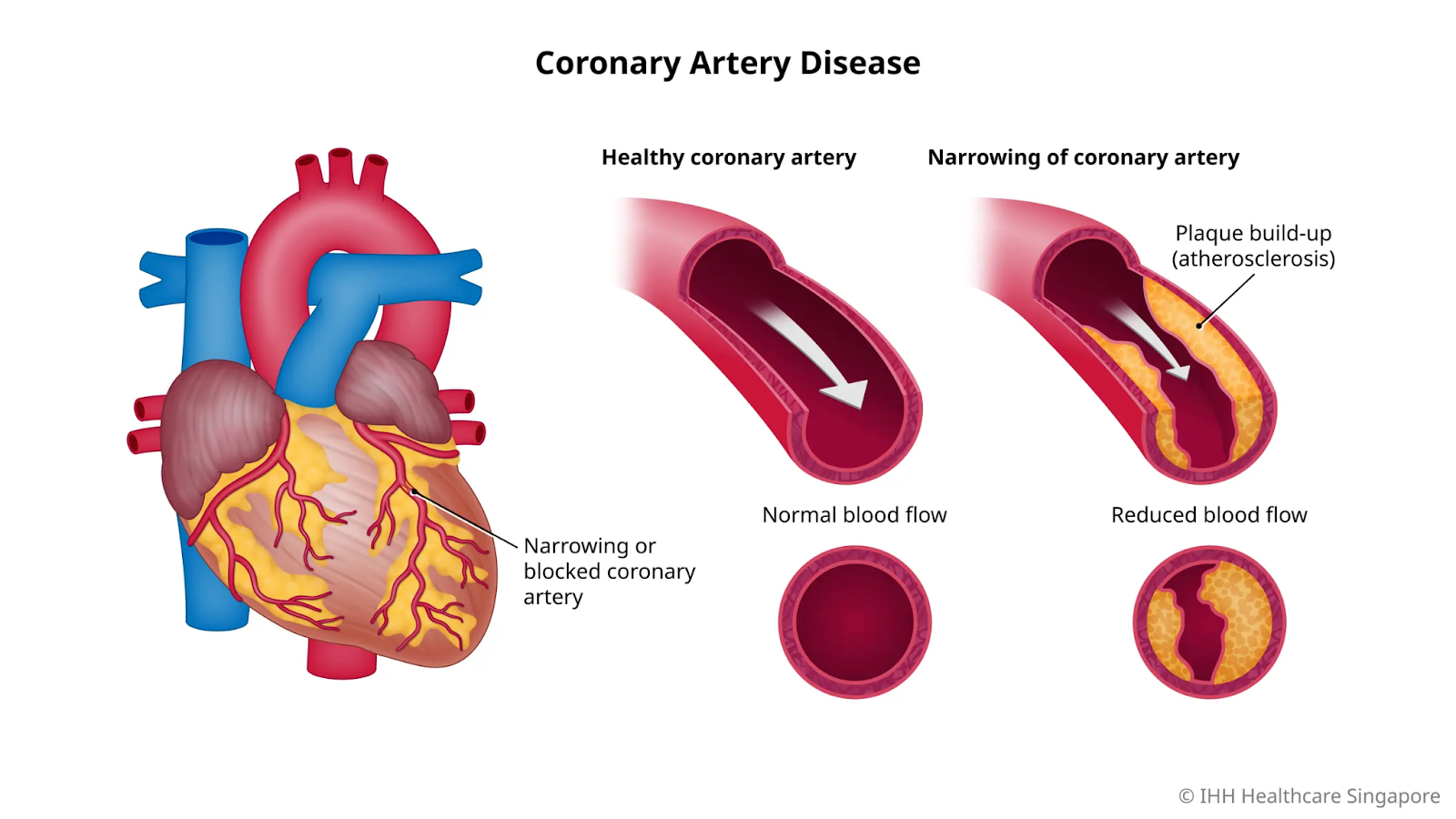
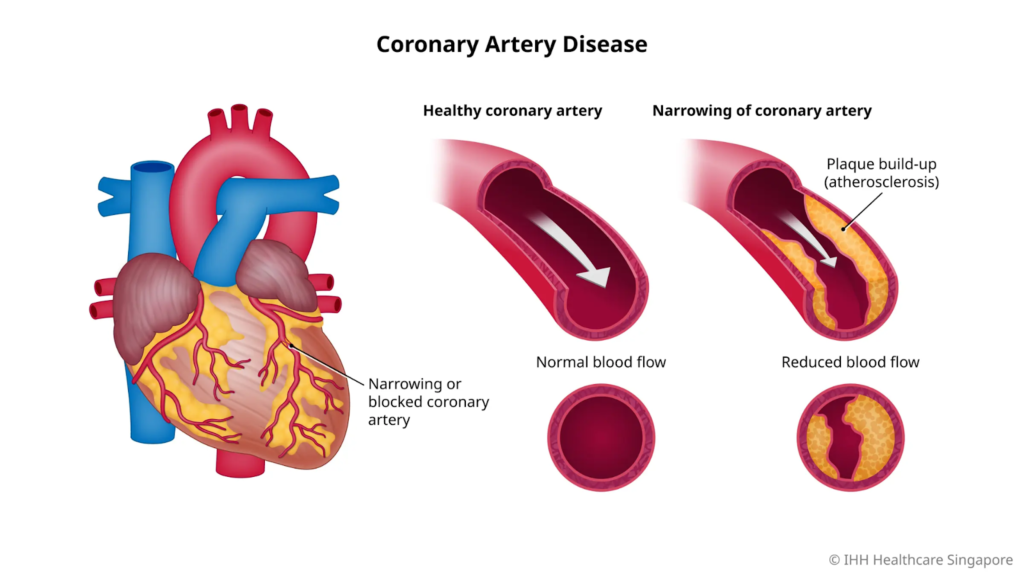
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) involves narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries due to plaque buildup, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle, potentially causing angina, heart attacks, or ischemia.
Types of Coronary Artery Disease
Types:
Stable angina:
Predictable chest pain from exertion, relieved by rest.
Unstable angina:
Sudden, severe pain at rest signaling acute risk.
Non-obstructive CAD:
Artery spasms or dysfunction without major blockage.
Acute coronary syndrome:
Includes heart attack from full rupture or clot.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
Symptoms:-
Common signs include angina (chest pressure, tightness, or pain radiating to arms, neck, jaw, or back), shortness of breath, fatigue, nausea, cold sweats, and dizziness; many cases are silent until a heart attack. Some cases remain asymptomatic until a heart attack occurs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes and Risk Factors: –
Main risk factors for coronary artery disease include both unchangeable elements like age and family history, as well as modifiable lifestyle and health issues that drive plaque buildup in arteries. Primarily atherosclerosis from cholesterol, fats, calcium, and inflammation buildup that harden and narrow arteries, potentially rupturing to cause clots; risks include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, obesity, inactivity, poor diet, and family history.
Non-Modifiable Factors:
Age increases risk significantly after 45 for men and post-menopause for women, while family history, especially early heart disease before age 50, raises susceptibility through genetic predisposition. Certain ethnic groups, such as Black, Hispanic, and South Asian populations, show higher prevalence.
Modifiable Factors:
High blood pressure damages artery walls; high cholesterol, especially LDL, promotes plaque; diabetes impairs vessel health; obesity (particularly abdominal fat) accelerates atherosclerosis; smoking constricts vessels and boosts clotting; physical inactivity weakens cardiovascular function; and unhealthy diets high in saturated fats, salt, and sugars compound these effects. Chronic stress and excessive alcohol further elevate risks.
Complications of Coronary Artery Disease
Complication:
Untreated CAD leads to heart attacks, arrhythmias, heart failure, or sudden cardiac death from restricted oxygen to the heart.
Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease
Prevention:
Adopt heart-healthy habits like quitting smoking, eating balanced diets low in saturated fats, exercising regularly (150 minutes weekly), controlling weight, managing cholesterol, and blood pressure via meds if needed, and limiting alcohol.
Public Awareness and Prevention Programs
Public Awareness: –
Campaigns like World Heart Day emphasize recognizing angina as a warning, promoting screenings and lifestyle changes; in India, NCVBDC and ICMR stress community education on risks amid rising urban cases.
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease Using Imaging Tests
Diagnosed with Imaging Test
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is diagnosed using various imaging tests that visualize artery narrowing, plaque buildup, or reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
1) Coronary CT Angiography (CCTA):-
This non-invasive CT scan uses contrast dye and rapid imaging to create detailed 3D pictures of coronary arteries, detecting blockages, plaque composition, and calcium scores with high sensitivity for early disease. It reliably rules out significant CAD in low-risk patients, often avoiding invasive procedures.
2) Invasive Coronary Angiography:-
Considered the gold standard, this catheter-based test injects dye into coronary arteries during X-ray imaging to directly measure stenosis severity and guide interventions like stenting. It’s reserved for high-risk or symptomatic cases due to its invasive nature.
Functional Imaging Tests:-
Stress tests with nuclear SPECT/PET perfusion imaging or cardiac MRI assess, identifying ischemia from CAD without directly visualizing arteries. Echocardiography evaluates wall motion abnormalities post-stress.
Main Difference Between Heart Attack, Stroke, Hypertension and Coronary Artery Disease
Heart attacks, strokes, hypertension, and coronary artery disease (CAD) represent distinct cardiovascular conditions with different mechanisms, affected organs, and timelines, though they are often interconnected through shared risk factors like high blood pressure.
Key Differences
| Sr. No. | Condition | Primary Mechanism | Affected Area | Acute / Chronic | Typical Outcome if Untreated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heart-Attack (Myocardial Infarction) | Sudden artery blockage by clot, starving heart muscle of oxygen | Heart muscle | Acute event | Muscle death, Heart failure, Arrhythmias |
| 2 | Stroke | A blocked or bust brain vessel, cutting off oxygen to the brain tissue | Brain | Acute event | Paralysis, Speech loss, Cognitive impairment |
| 3 | Hypertension | Chronically elevated blood pressure straining vessels | Entire Vascular system | Chronic condition | Artery damage leading to CAD, stroke, and Kidney failure |
| 4 | Coronary Artery Disease | Gradual plaque buildup narrowing heart arteries | Coronary Arteries | Chronic progression | Angina, eventual heart attack |
Interconnections Between Cardiovascular Conditions
Interconnections: Hypertension accelerates CAD by damaging artery linings, promoting plaque; CAD can trigger heart attacks via rupture; both heighten stroke risk through clots or weakened vessels. All share risks like smoking, obesity, and diabetes, emphasizing prevention through lifestyle and blood pressure control.