A Stroke is a sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain, causing brain cell death and potential long-term disability or death. It’s a medical emergency requiring immediate action.
Types of Stroke
Types:-
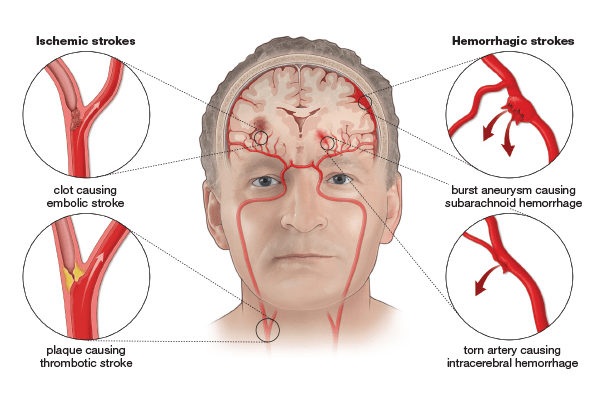
Strokes are mainly classified into two categories:
Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic (about 87% of cases), caused by a blood clot blocking a brain artery. Subtypes include thrombotic (clot forms in brain artery), embolic (clot travels from elsewhere).
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic strokes from a ruptured blood vessel, causing bleeding into or around the brain, triggered by high BP or aneurysms.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Transient ischemic attacks (TIA) are brief “mini-strokes” temporary blockage, resolving within 24 hours but signal future risk.
Causes of Stroke
Causes:-
- Ischemic strokes often result from clots due to atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, or artery narrowing.
- Hemorrhagic strokes stem from high blood pressure, aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations leading to vessel rupture.
Risk factors include hypertension, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol and heart disease.
Symptoms of Stroke
Symptoms:-
Common signs are sudden numbness, weakness (especially one side), confusion, trouble speaking / understanding, vision loss, severe headache, dizziness, or loss of balance.
Use FAST:-
Face drooping
Arm weakness
Speech difficulty
Time to call emergency 108 /911
Symptoms vary by brain area affected, with women sometimes experiencing atypical signs like fatigue.
Treatment of Stroke
Treatment:-
Immediate care involves clot busting drugs like tPA for ischemic strokes within 4.5 hours or mechanical thrombectomy.
Hemorrhagic cases may need surgery to repair vessels and control bleeding; long term rehab includes therapy and medications like blood thinners.
Treatment depends on type and speed of intervention.
Stabilize the Patient
Stabilize the Patient:- Help them sit or lie on their side with head slightly elevated to aid breathing and prevent choking if vomiting; loosen tight clothing but do not give food, drink or medications. Note symptoms onset time precisely treatment eligibility. If stop breathing or become unresponsive, start CPR (hands only, 100 to 120 compressions/min.), then provides ambulances.
Prevention of Stroke
Prevention:-
Control risks by managing blood pressure, quitting smoking, exercising, eating healthily and treating conditions like diabetes or atrial fibrillation.
About 80% of strokes are preventable with lifestyle changes and medications like statins or anticoagulants.
Regular check-ups aid early detection.
Rehabilitation After Stroke Recovery
Rehabilitation After Stroke Recovery:-
Stroke rehabilitation focuses on restoring function, independence, and quality of life after the initial recovery phase, tailored to individual needs across acute, subacute, and chronic stages.
Physical Therapy
Physical Therapy:-
Physical Therapy improves strength, balance, mobility and gait through exercises like proprioceptive training, dual-task activities, and aerobic exercise.
Constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT) and robot-assisted therapy promote repetitive use of affected limbs, enhancing motor recovery.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational Therapy:-
This therapy targets daily activities (ADLs) such as dressing, eating and cooking by refining fine motor skills and adapting environments.
Mirror therapy and functional electrical stimulation (FES) aid hand function and muscle control.
Speech Therapy
Speech Therapy:-
Speech and language therapy (SLT) addresses communication, swallowing and cognitive issues, improving speech clarity and social interaction.
Other Options and Supportive Care
Other options and supportive care:-
Virtual reality, hydrotherapy and music therapy boost engagement, coordination, and mood.
Cognitive rehabilitation targets memory and problem-solving.
Psychological counseling manages depression and anxiety; community programs ensure long term maintenance.
Difference Between Heart Attack and Stroke
Difference between Heart attack and Stroke:-
Heart attacks and Strokes are both emergencies caused by vascular blockages or ruptures but affect different organs; heart attacks damage heart muscles while strokes damage brain tissue.