Bone cancer refers to malignant tumors that originate in the bone tissue, either primary (starting in the bone) or secondary (spread from other cancers). It is rare, affecting bones like the long bones in arms and legs, and requires early detection for better outcomes.
Definition
Bone cancer involves uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in bone tissue, destroying normal bone and potentially spreading elsewhere. Primary types are less common than metastatic cases from cancers like breast or prostate.
Causes and Risk Factors
Exact causes remain unknown, but risks include genetic disorders (e.g., Li-Fraumeni syndrome), prior radiation exposure, and certain bone conditions like Paget’s disease. Most patients lack clear risk factors.
Main Types
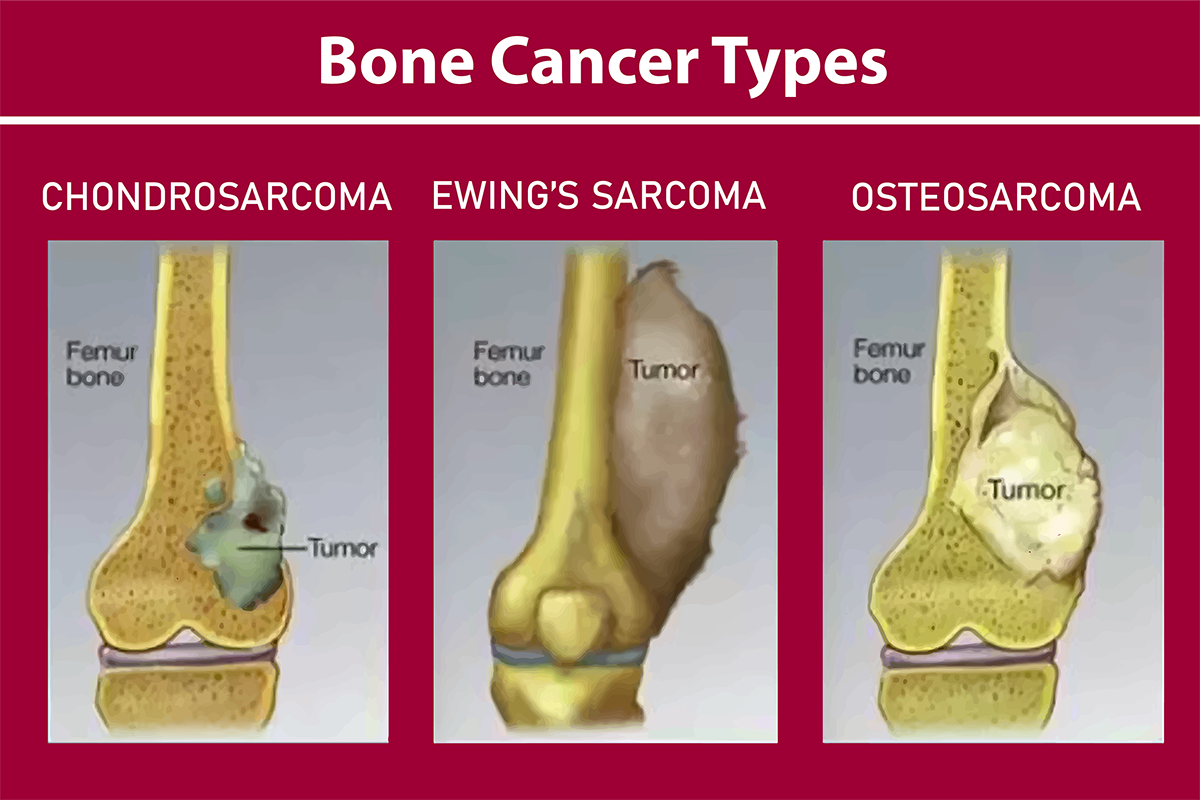
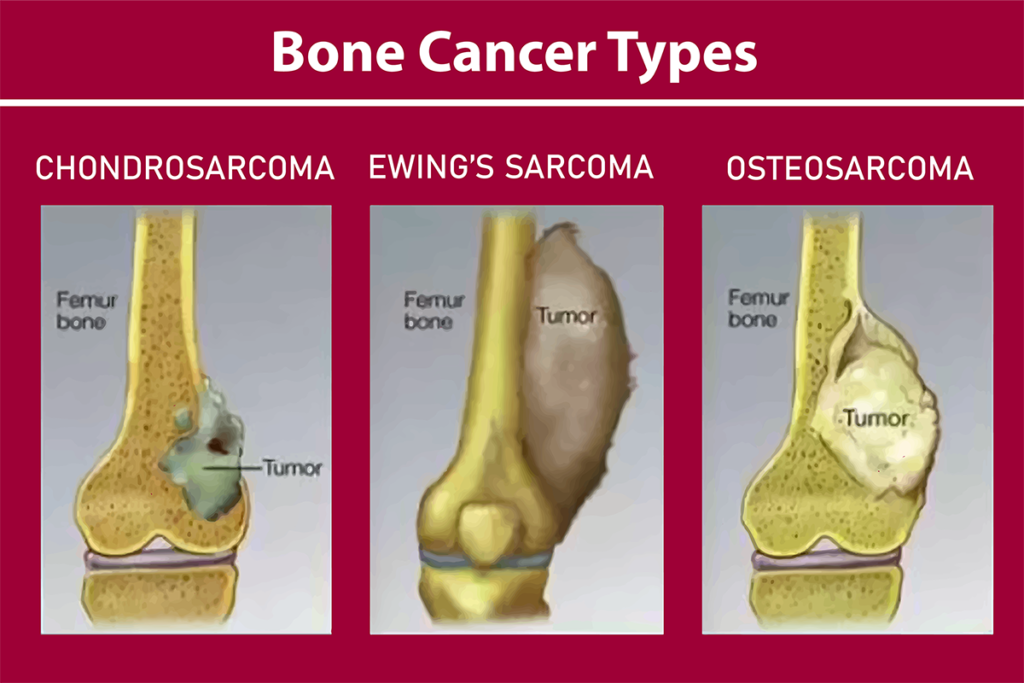
Osteosarcoma:
Common in children and teens, it affects long bones.
Ewing sarcoma:
Fast-growing, mainly in children and teens.
Chondrosarcoma:
Arises from cartilage, more in adults.
Symptoms
Persistent bone pain (worse at night), swelling or lumps near the bone, fractures from minor trauma, fatigue, and weight loss. Early symptoms mimic injuries, delaying diagnosis.
Laboratory Diagnosis and Methods
Biopsy (needle or surgical) confirms cancer type by examining tissue under a microscope—key for definitive diagnosis. Blood tests check general health and markers like alkaline phosphatase.
Imaging Diagnostics
X-rays detect bone abnormalities first; MRI/CT/PET scans assess tumor size/location/spread; bone scans identify metastases.
Prevention Measures
No sure prevention exists, but reduce risks by avoiding unnecessary radiation, treating bone infections promptly, and having regular check-ups for high-risk groups. A healthy lifestyle supports overall bone health.
Control Measures
Early screening for at-risk individuals (e.g., genetic syndromes), surveillance imaging, and multidisciplinary care limit spread.
Treatment
Surgery removes tumors (limb-sparing preferred); chemotherapy shrinks tumors/prevents spread; radiation for inoperable cases. Targeted therapies are emerging for specific types; survival is up to 70% if early-stage.
Public Awareness
Campaigns educate on symptoms like unexplained pain, stressing early medical consultation via posters/social media. Focus on rarity but treatability. Bone cancer awareness campaigns focus on rare primary bone tumors like osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma, emphasizing early detection through symptom recognition. Major efforts occur during dedicated months or weeks globally and in India.
Bone Cancer Awareness Week, 7 to 13 October, by Bone Research Trust promotes symptoms, early diagnosis, and research via events, stories, and ribbons. Sarcoma/Bone Cancer Awareness Month (July) features yellow ribbons, light-ups, races, and education by groups like the Sarcoma Foundation of America.
Community Engagement
Local health drives, survivor stories, and school programs to promote symptom recognition and screening uptake. Engaging communities in bone cancer prevention builds awareness of risk factors, promotes early detection, and fosters healthy behaviors since no direct vaccine or cure-all exists. Strategies leverage partnerships, education, and local events for sustained impact.
India-Specific Initiatives
July marks Sarcoma and Bone Cancer Awareness Month with calls for public education, rural screenings, and policy advocacy by experts like Dr. Chetan Anchan. The India Cancer Society runs “Raho cancer se do kadam aage” (“Stay two steps ahead of cancer”) campaigns in multiple languages across states for symptom awareness and myth-busting.
IEC Materials
Information, education, and communication tools include pamphlets, videos, and infographics in local languages (e.g., Marathi, English, Hindi, etc.) in India on symptoms/diagnosis. Distribute IEC materials in local languages, run social media drives, and train community health workers for door-to-door education on early signs and myths.
Role of Public Health Department
The department tracks incidence via surveillance, funds screenings and treatments, runs awareness campaigns, trains providers, and integrates into cancer registries for policy-making.