Epidemiological Parameters in Malaria
Aim
Epidemiological indices in malaria are key quantitative measures used to monitor malaria prevalence, evaluate control efforts, and track trends in endemic areas. These parameters help assess the disease burden and guide public health policy and interventions.
1. ABER – Annual Blood Examination Rate
- Definition: Proportion of blood smears collected and examined in a year through active case detection (ACD) and passive case detection (PCD).
- Note: Temporary collections such as mass or contact surveys are not considered.
- Formula:

Standard Value:
- 10% is the standard benchmark.
- Below 10% → Dangerous.
- Above 10% → Good.
Timeframe: Calculated yearly.
2. MBER – Monthly Blood Examination Rate
Definition: Same as ABER but calculated monthly.
Formula:

Standard Value:
- 1% is the benchmark.
- Below 1% → Dangerous.
- Above 1% → Good.
Standart value of MBER is 1 % . Below 1% is dangerous . More than 1% is good . MBER = Monthly blood examination rate = It is calculated as like ABER but one month only .
3. API – Annual Parasite Incidence
- Definition: Number of confirmed malaria cases per 1,000 population in a year.
- Formula:
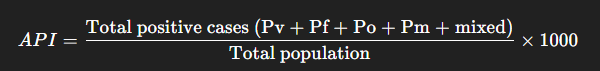
Standard Value:
- Less than 2 → Safe.
- 2 or more → Dangerous.
Timeframe: Calculated annually.
4. SPR – Slide Positive Rate
- Definition: Proportion of positive malaria cases among all examined blood smears/RDK (Rapid Diagnostic Kits).
- Formula:
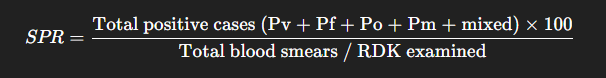
Standard Value: Less than 4%.
SPR is variable or not constant , because it is depend upon the transmission period . Standart value of SPR is less than 4% ,then no problem in that area .It is always taken for particular period { eg one month or one year etc }
5. SFR – Slide Falciparum Rate
- Definition: Proportion of Plasmodium falciparum cases (including mixed infections with Pf) among all examined samples.
- Formula:
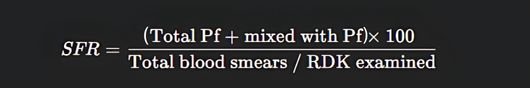
- Standard Value: Less than 0.5%.
- More than 0.5% → Problematic area.
6. PFR – Positive Falciparum Rate (PF %)
- Definition: Proportion of falciparum-positive cases among all malaria-positive cases.
- Formula:
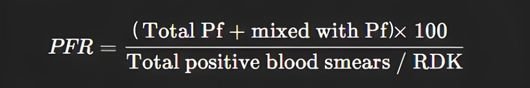
- Standard Value: Less than 30%.
- Greater than 30% → Indicates a problematic area.
7. AFI – Annual Falciparum Incidence
- Definition: Number of falciparum cases per 1,000 population in a year.
- Formula:
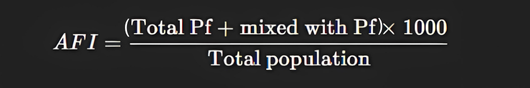
Importance:
- Helps track the burden of P. falciparum.
- Supports evaluation of elimination efforts.
Benchmark: If AFI < 3 → Transmission intensity is low (i.e., 3/1000 population).
AFI help in tracking the burden of P. falciparum , supporting evaluation of elimination efforts . If AFI is less than 3 ,then it ‘s means 3/1000 population , highlighting transmission intensity.